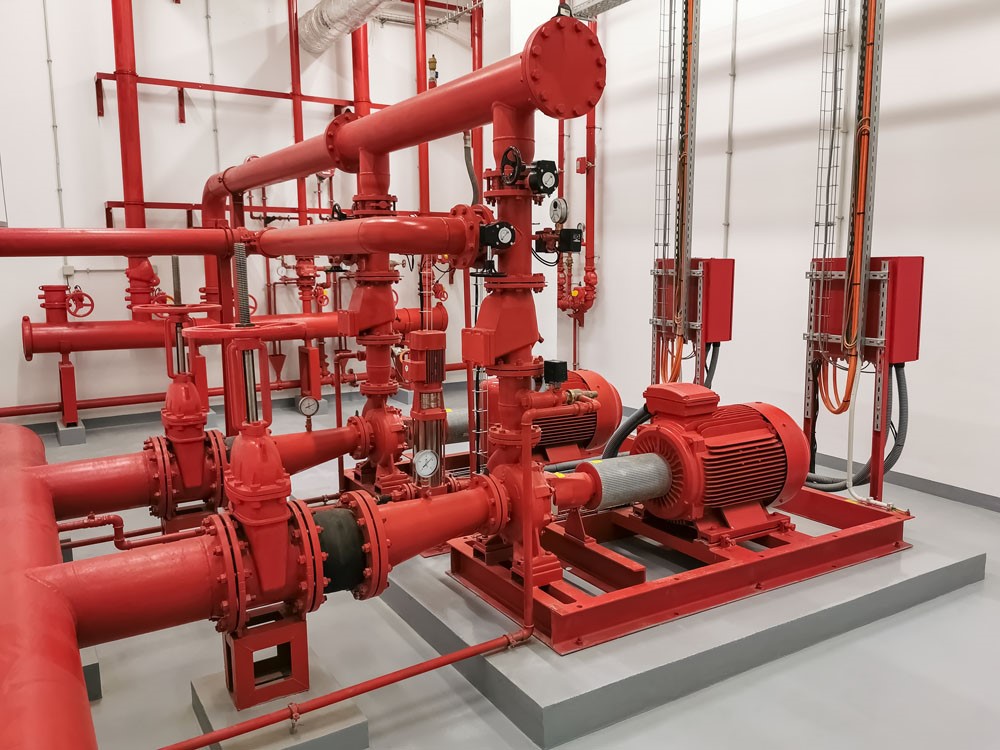
Fire Protection Engineering
Our fire protection engineering services protect life, property, and your ability to continue successful business operations. We offers a comprehensive suite of fire protection engineering services including full code design, performance-based design, and demonstrated regulatory compliance. Our specialty in fire protection engineering services has developed hand-in-hand with our focus on sustainable building engineering and design.
Our vast area of fire and life safety protection includes:
- Fire Suppression Systen Design, Review & Implimentation
- Architectural Life Safety System Design And Consultation
- Fire Alarm System Design & Review & Implimentation
- Fire Safety Audits/ Inpsection
- Civil Defense Approval
- Emergency Evacuation Diagram & Procedures
- Prepare Bill Of Quantity (BOQ) And Recommend Materials
- Developing Effective Fire Protection System For Older And Heritage Buildings
Our Target Areas,
- High Rise Buildings
- Residential Buildings
- Covered and Open Malls
- Hospitals
- High-piled Combustible Storage Areas
- Deep Underground Buildings
- Airport
- Repair Garages
- Parking Garages
- Theaters and Stages
- Auditorium
- Stadium
- Amusement Buildings
- Gas Stations
- Children’s Play Stations
- Oil Refineries
1. Fire Suppression System Design, Review & Implimentation

We are experts in designing all kind of automatic and manual fire suppression system for organizations, businesses, buildings and structures of all types and sizes as per Civil Defense requirements according to all international and local codes such as NFPA 13, NFPA 14, NFPA 20, NFPA 10 and the Saudi Building Code SBC 801.
Common design features of sustainable buildings, including photovoltaic designs, battery storage, roofing materials, energy efficient insulation, and other considerations, can come with an increased fire safety risk if they are not carefully considered and properly protected.
- Fire sprinkler system design as per NFPA 13 and SBC 801
- Fire water calculation through pipe scheduling method and hydraulic calculation method as per NFPA 13
- Class 1, Class 2, Class 3 standpipe and hose cabinet design as per NFPA 14 and SBC 801
- Design both dry and wet fire suppression systems.
- Recommend the installation of automatic or manual fire suppression system as per the code requirement
- Design Warehouse fire suppression systems using ESFR and In-Rack sprinkler systems
- Design and recommend the flow and pressure required for all the pumps including Diesel, Electric and Jockey pumps and recommend the location and fire resistance rating of fire pump room as per NFPA 20 and SBC 801
- Design fire water storage tank in accordance with standards for both above-ground and underground environments and calculate the volume needed to completely suppress a fire for the structure
- Calculate the pipe size for the entire system using pipe scheduling method as per NFPA 13
- Design the fire sprinkler system's test line to assess the system's performance on a regular basis.
- Conduct a hazard analysis on the structure to ascertain the precise type of fire protection system needed.
- Design Civil Defense connection to the fire sprinkler system as per NFPA 13, NFPA 14 and SBC 801. According to the code, single-story buildings with an area of more than 2000 square feet (185 m2) and buildings located in remote places are exempt from this civil defense connection.
- Recommend the type, quantity and location of fire extinguishers to be placed in the area as per NFPA 10
- Review of contractor design, carryout materials selection and prepare quotation
- Design private fire hydrant system where public fire hydrant systems are not present and where the code SBC 801 suggest.
- Undertake commissioning of fire protection system
- Designs utilizing Building Information Modeling (BIM)
2. Architectural Life Safety Systems Designing and Consulting

Life safety is a complex discipline of vital concern to building design and construction. Our team evaluates the effectiveness of life safety designs and methods in assuring the occupants' safety inside various buildings and structures by applying scientific and engineering concepts along with a solid understanding of international and local codes and standards like NFPA 101 and SBC 801. We offer affordable guidance and support to help accomplish design goals in a safe and cost-effective manner.
Scope of Life Safety System designing
- Recommend the number of exits to be required for a building and their separation distance as per the code requirement
- Evaluate and confirm the staircase width and capacity, corridor width, stairway landing width, ceiling height and size of refuge area is enough to accommodate the specified number of occupants in the building.
- Confirm the size, spacing and type of the door to be used as per the code requirement and install fire door of required rating and with panic hardware where code suggest.
- Check whether emergency lights are placed at proper locations and satisfies the quality of illumination to enable easy exit of occupant from the building in case of emergency.
- Check that the handrail and rail guards meet the standards.
- Calculate the exit access travel distance and common path distance and recommend the quantity and location of exit doors as per the calculated value.
- Ensure that each wall and opening of the building satisfies the fire resistance rating stated by the code.
- Ensure Emergency exit signs are of required dimensions and with sufficient backup power specified by the code and we also recommend the location of Emergency exit and directional exit signs.
- Deeply examine the design and recommend the requirement of fire dampers and stairway pressurization.
3.Fire Alarm System Design Review & Implimentation

We are able to design both addressable and non-addressable fire alarm system for both high-rise and non-high-rise buildings and structures in accordance with local and international codes such as NFPA-72 and the Saudi Building Code SBC 801 which satisfy Civil Defense requirements.
Scope of Fire Alarm System Design,
- Recommend the type of detector to be used in a location after strict evaluation of the area and the belonging contents.
- Ensure Manual Call Points are located at a distance of 1.5m from each entrance or exit and are installed at a max height of 1.2m from the floor level and is available at a travel distance not exceeding 60m and ensure its access is unobstructed as specified in SBC 801.
- Confirm required primary power supply and secondary backup power for the fire alarm panel as specified in NFPA-72.
- Recommend the requirement of addressable or non-addressable fire alarm panel as per the area consideration.
- Recommend the installation of visible and audible alarms and their locations as per the code after the evaluation of the area.
- Ensure that the audible alarms deliver maximum sound pressure for the required time.
- Verify zone division is done properly and only specified number of detectors are supplied in each zone
- Install advanced mode of detectors like multi detectors, beam detectors etc. in specialized locations such as atrium, elevator room etc.
- Recommend the installation of smoke controlling measures.
4.Fire Safety Audits/ Inspection
We are experts in undertaking fire safety audit/ inspection of buildings or organization. The audit assesses the building for compliance with the Saudi Civil Defense Requirements for certification in accordance with international and local building codes and standards such as NFPA 10, NFPA 13, NFPA 14, NFPA-72, NFPA 101 and SBC 201, SBC 801 and SBC 901. This guarantees that life safety, fire protection, and fire alarm system installation and operation comply with applicable codes and standards. The audit findings also provide recommendations on how to remedy any non-compliances that were identified .
Our audit reports help demonstrate compliance with the relevant codes to building approval officers, certifiers, councils or insurance companies. Adherence to legal requirements guarantees that your structure or location is suitable for use and poses the least amount of risk to people's lives, property, or content.
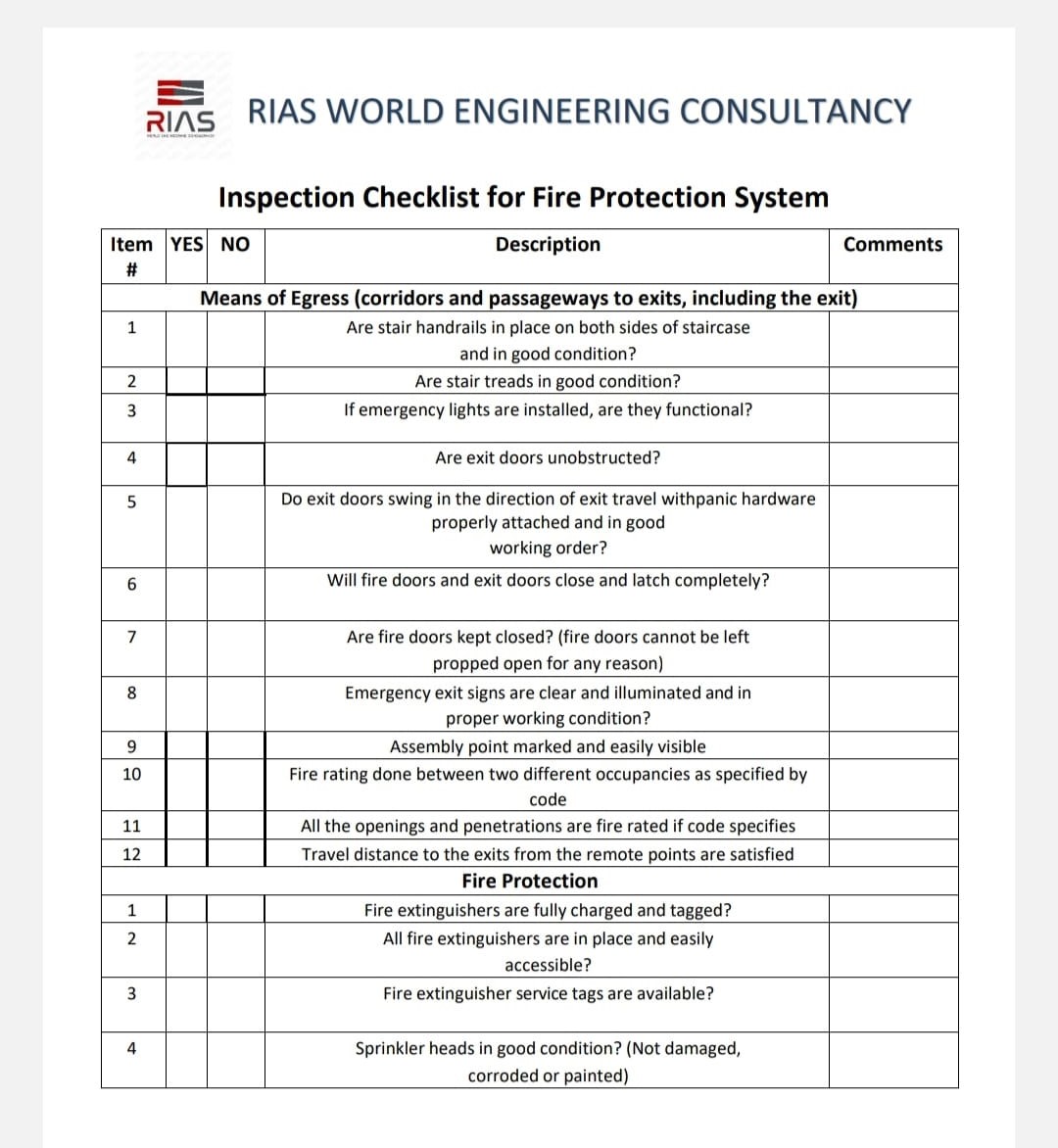
Our inspection area includes
- Inspection for passive and active fire protection system
- Smoke, heat, multiple detectors and manual fire alarm call point locations
- Pressure and flow characteristics of fire hose reel and landing valves.
- Sprinkler head pressure and flow characteristics
- Pressure and flow characteristics of Diesel pump, electrical pump and jockey pump.
- Riser pipe characteristics and made
- Egress dimensions
- Compartmentation zones
- Fire alarm cause and effect
- Emergency light and exit sign locations
- Dimension of stair, shaft, door, handrail etc.
- Location of visual and audible fire alarms and their connectivity.
- Spacing of detectors and sprinklers are sufficient to cover complete area
- Emergency egress pathways are away from obstructions.
- Smoke control measures
- Number of exit and exit dimensions
- Specified fire rating for walls and openings
- Light intensity of emergency light and visual alarms
- Primary and back power supply of fire alarm panel
- Civil defense connection and other piping dimensions and layout
- Selection and location of fire extinguishers.
5.Civil Defense Approval

Saudi Arabian laws mandate that civil defense must approve all structures based on how well they adhere to the design and installation of fire protection, life safety and fire alarm systems.
Regardless of the size and complexity of a building, a fire strategy has a crucial part to play in demonstrating compliance with fire safety legislation and providing operators with a record of the design. Fire safety design, and the development of an appropriate fire strategy, relies upon understanding the basis of design guidance and the ability to demonstrate that the project complies with local regulations.
We determine the most appropriate design guidance for a project so that it can meet the requirements of those regulations with minimal compromise to the project.
In the event that a project is unable to comply with the guidelines, we give practical fire engineering solutions by utilizing a variety of research outlets and our technical experience.
6.Emergency Evacuaton Diagram & Procedures

According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), Even if evacuation may be necessary in any kind of emergency, this should still be determined case-by-case. We are experts in designing Emergency Evacuation Map for any kind of building or industry. We are also experts in reviewing the evacuation plan already made and recommend the updations to be made.
We create emergency evacuation plans that, in accordance with "world's best practice" in fire and life safety management, maximize occupant life safety within the development.
Initially, our team will survey both under construction sites and occupied buildings to identify the necessary evacuation plans from every area of the site, the position of the functioning fire apparatus, the orientation of the site in relation to the locations of all accessible exits, and the necessary assembly locations. Then we prepare procedures and operating manuals written in clear and unambiguous language tailored to the express needs of users which avoids confusion.
All possible crises and threats to life safety are taken into account in our evacuation diagrams, such as the possibility of an internal or external fire, a gas leak, a bomb threat, a medical emergency, or the discovery of a suspicious package.
Steps of preparing an evacuation plan;
Step 1: Evaluate the EmergencyAssess the vulnerability of your workplace to a specific emergency. Identify the need for greater resources or assistance, such as special equipment and/or extra facilities for handling a critical emergency. This is especially crucial for workplaces in hazardous environments.
Step 2: Determine Exit RoutesMap out exit routes in the floor plans. Follow these best practices from OSHA while determining exit routes:
- Exit routes must be as far away as practical from each other.
- Doors should swing out in the evacuation direction and be unlocked from the inside.
Scout a potential safe area or assembly point. Ask the following questions while identifying the same:
- Is this area usually and relatively safe?
- Is this area well-lit?
- Is it easy to access emergency services from this area? (the area is near a hospital, etc.)
- Does this area have good cell service / signal?
- Will employees have difficulty finding this area once they exit the workplace?
- Could this area ever be obstructed during an emergency? (trucks blocking the road, etc.) Point up any situations in which the area might still be dangerous or where an emergency could potentially affect the region.
Once you have decided on the exit routes and on the designated safe area, develop a step-by-step evacuation procedure for each area in the workplace. For example, if an employee is in room 1, they must follow specific steps to go through exit route 1 and then get to the designated safe area.
If you have more than 25 employees, consider establishing a procedure for employees to digitally check-in and verify that they are safe (as opposed to or to supplement the in-person headcount done by the evacuation wardens).
Step 5: Discuss with EmployeesHold a meeting with employees to discuss the appropriateness of exit routes, safe areas, and evacuation procedures. Note down suggestions, comments, and points for further clarification. Revise the emergency evacuation plan based on employee feedback. Then, present the revised emergency evacuation plan to employees for approval.
Step 6: Assign ResponsibilitiesAssign evacuation officers, wardens, and assistants. Establish a chain of command:
- Evacuation Officer 1 – the coordinator or leader of the evacuation; has the authority to make decisions during emergencies; and is responsible for coordinating with outside emergency services
- Evacuation Officer 2 – If Evacuation Officer 1 is unavailable during an emergency, Evacuation Officer 2 assumes the role of evacuation coordinator.
- Evacuation Officer 3 – If both Evacuation Officer 1 and 2 are unavailable during an emergency, Evacuation Officer 3 assumes the role of evacuation coordinator.
- Evacuation Wardens – Wardens direct employees to proper exit routes until they reach the designated safe area. OSHA recommends that for every 20 employees, you assign one evacuation warden. Alternatively, you may assign one evacuation warden per floor or for each area in the workplace.
- Assistants – They check if employees are following the warden and if anyone is left behind or needs help. They may also monitor the safety of employees assigned to shut down operations before evacuating.
Once the plan has been approved by employees, distribute copies (preferably digital) to all employees (including part-time) as well as frequent visitors and third-party workers.
Step 7: Conduct Training ExercisesSet a date for employee training on the specific emergency evacuation plan. This may include test runs, drills, and other practical exercises. Set intervals for training (e.g., every 3 months).
It would also be very beneficial to conduct your own internal training make involving every employee. With this, employees can have more detailed idea about emergency evacuation, ensuring all employees are aware of the right safety steps.
Step 8: Review and Update the Plan as NeededChanges in the workplace will also warrant a review and update of the plan. Additionally, feedback or results from training exercises can lead to major revisions in the plan. For each update and revision, employees must be notified and retrained accordingly.
7.Prepare Bill Of Quantity (BOQ) And Recommend Materials

A bill of quantities, or BOQ is like a detailed shopping list for a construction project. Imagine you’re building a house and you need to know exactly how much of each material such as bricks, cement, and wood you will need. The BOQ does just that. It lists how much of each item is required for the project and estimate the total project cost.
BOQs play a crucial role in making the tendering process more uniform, pricing more precise, and project costs more predictable. They serve as a cornerstone document, not only during the construction phase but also for the long-term management and development of projects. We are able to prepare customer specific and site specific BOQ and recommend quality materials with a feasible rate.
Functions of BOQ;
1. Standardizing the tendering processIt allows contractors to prepare precise cost estimates based on the same information.
2. Facilitating tender analysis- BOQs enable thorough tender analysis, where both total project costs and individual rates can be evaluated.
- This ensures that contractors submit complete, compliant bids that align with specifications and meet budgetary goals.
- This helps in predicting and managing project expenditures effectively.
- BOQs provide detailed schedules and breakdowns, offering owners visibility into cash flow needs over various project cycles.
- BOQs act as the foundation for the final contract between the client and the contractor. In case of disputes or claims during construction, they provide a reference point for conflict resolution.
- By specifying materials and labor, BOQs create transparency around scope and pricing, reducing errors and misunderstandings.
- This ensures that all parties have a clear understanding of the project’s requirements.
- The comprehensive information within a BOQ becomes a valuable record for future maintenance, repairs, and potential expansions.
- This saves time and effort compared to re-quantifying for subsequent work on the project.
- Project information
- Items
- Item differentiation
- Unit of measurement
- Quantities
- Unit costs
- Total item cost
- Terms and conditions (optional)
- Step 1. Initial project documentation
- Step 2. Itemisation and categorisation
- Step 3. Quantify with costs
- Step 4. Quality control
- Step 5. Compliance and standards
- Step 6. Final compilation
8.Developing Effective Fire Protection System For Older And Heritage Buildngs

In existing older and heritage buildings, it is crucial that the building is managed appropriately so that the principles of the fire strategy are maintained. In most buildings this can be a simple undertaking by end users, but in more complex buildings it is beneficial for a fire engineer to provide consideration of detailed operational issues.
Most older or historically significant buildings lack a clear and comprehensive fire plan because of their age or prolonged development. This causes barriers and difficulties for continued administration and future renovation. We are able to evaluate current structures, regardless of their age or complexity, and offer effective fire protection tactics that clarify building management and identify potentially beneficial opportunities for renovation works.
Most older or historically significant buildings lack a clear and comprehensive fire plan because of their age or prolonged development. This causes barriers and difficulties for continued administration and future renovation. We are able to evaluate current structures, regardless of their age or complexity, and offer effective fire protection tactics that clarify building management and identify potentially beneficial opportunities for renovation works.


